Dissolved air flotation (DAF): Is it the best way to treat your wastewater?
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) for industrial wastewater treatment is a water clarification process that uses micro-bubbles to remove impurities and solids. The process is ideal for removing light impurities and solids that tend to float and suspend ( such as TSS, BOD, COD, and pollutants) in your wastewater.
The DAF process is in contrast to water treatments that focus on sedimentation to remove settled solids. However, most DAF systems account for some sedimentation and settled sludge removal.
DAF systems separate solids, oils, greases, and other impurities from water. The clean water can be reused or discharged. DAF is used for a variety of goals, including:
• Treatment to meet discharge regulations
• TSS Removal
• Water recovery and reuse
• Pretreatment to reduce loading on downstream biological treatment systems
• COD & BOD Removal
• Polishing of biologically treated effluent
• Thickening of slurry
• Pretreatment for desalination plants utilizing reverse osmosis
How Does Dissolved Air Flotation Work?
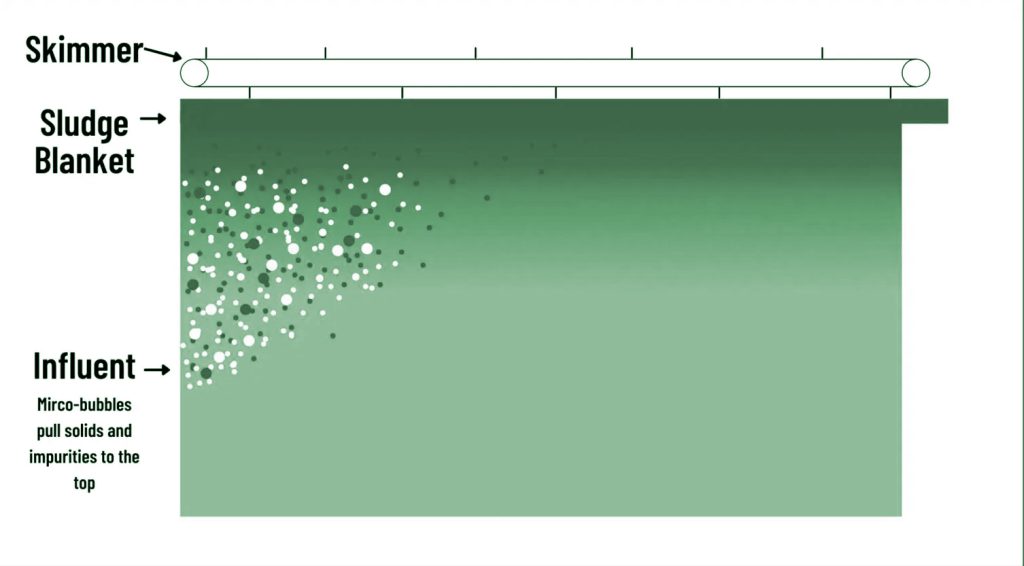
DAF uses micro air bubbles (30-50 micron) that attach to impurities and flocculated particles and float them to the water’s surface. Then a skimming system removes the sludge to a desludging trough, and clean water is recovered.
The clean water can be reused for process or discharged, and some of it is recycled back to the DAF process.

DAF Clarification Steps
First, clean water needs to be accessible for a DAF system to startup. Clean water is necessary because DAF systems pressurize the water and mix it with pressurized air. Under pressure, the air dissolves, and when de-pressured, micro-bubbles form. The micro-bubbles are necessary to the cleaning process.
So, the first step is to fill the DAF system with clean water. If you fill the DAF unit with wastewater, you’ll likely discharge wastewater for a long time. Plus, you risk damaging the recirculation pump and air saturation system.
Once clean water is in the system, a recirculation pump pulls some of the clarified water to a pressurization-saturation system. Next, the water is pressurized by a pump and mixed with pressurized air. Under this pressure, the air dissolves in the water.
Now the saturated water flows under pressure to the clarification tank. In the clarification tank, the pressure releases, and micro-bubbles form.
The micro-bubbles attach to the impurities from the incoming wastewater stream and pull them to the top. When sediment rises, a floating sludge blanket forms on top of the water within the clarifier.
Next, a skimming system gently removes the sludge from the top of the water.
Finally, clean water is recovered through a supernatant system. Basically, the clean water comes out of a discharge point below the floating sludge and above the settled sludge.
Do DAF Systems Manage Settled Sludge?
Most systems account for and manage settled sludge. DAF systems are ideal for wastewater streams that contain solids that float and settle.
In general, you’ll find most manufacturers include a sediment compartment or basin with a sludge extraction system.

Chemical Treatment with DAF Systems
Coagulants and flocculants are regularly used to pretreat wastewater before it enters a DAF system.
Like other wastewater treatment methods, a DAF system can benefit from particles that bind due to flocculants. The skimming systems can remove a thicker, more dewatered sludge that may need little to no further dewatering.
You’ll find that flocculation tubes are often used to condition the wastewater with chemical treatment before entering DAF systems. We noted this in the clarification steps.
What Applications are DAF Clarifiers Used to Treat?
Due to the DAF clarifier design and technology, they can service many industries. DAF technology can incorporate into custom-built clarifiers to fit different water flows with low to high impurity levels. In general, they’re ideal for wastewater streams with oil, grease, and impurities that float or suspend.
DAF systems can service but are not limited to the following industries & production processes:
• Oil, Petrochemicals, and Refineries
• Energy Production
• Pharmaceutical & Cosmetics
• Mining, Quarries, and Aggregate Production
• Tunneling & Boring
• Meat & Poultry Processing
• Slaughterhouse Processing
• Fish & Crustacean Processing
• Dairy Industry
• Convenience Food
• Potato Processing
• Fruit Processing
• Vegetable Processing
• Bakeries & Confectionaries
• Brewing (Alcoholic & Non-Alcoholic Production)
• Textile Finishing and Dyeing
• Tannery Production
• Stone Processing
• Tar Sand & Oil Sand
• Heavy Metal Removal
• Industrial & Commercial Laundries
• Pulp & Paper Production
• Algae Removal & Desalination Pretreatment
• Pretreatment for Downstream Biological Treatment Systems
Is a DAF System the Best Way to Treat Your Wastewater?
It’s hard to say without knowing the details of your application. There are many different DAF system designs to treat variable wastewater solids content and flow rates.
